-
Original research article
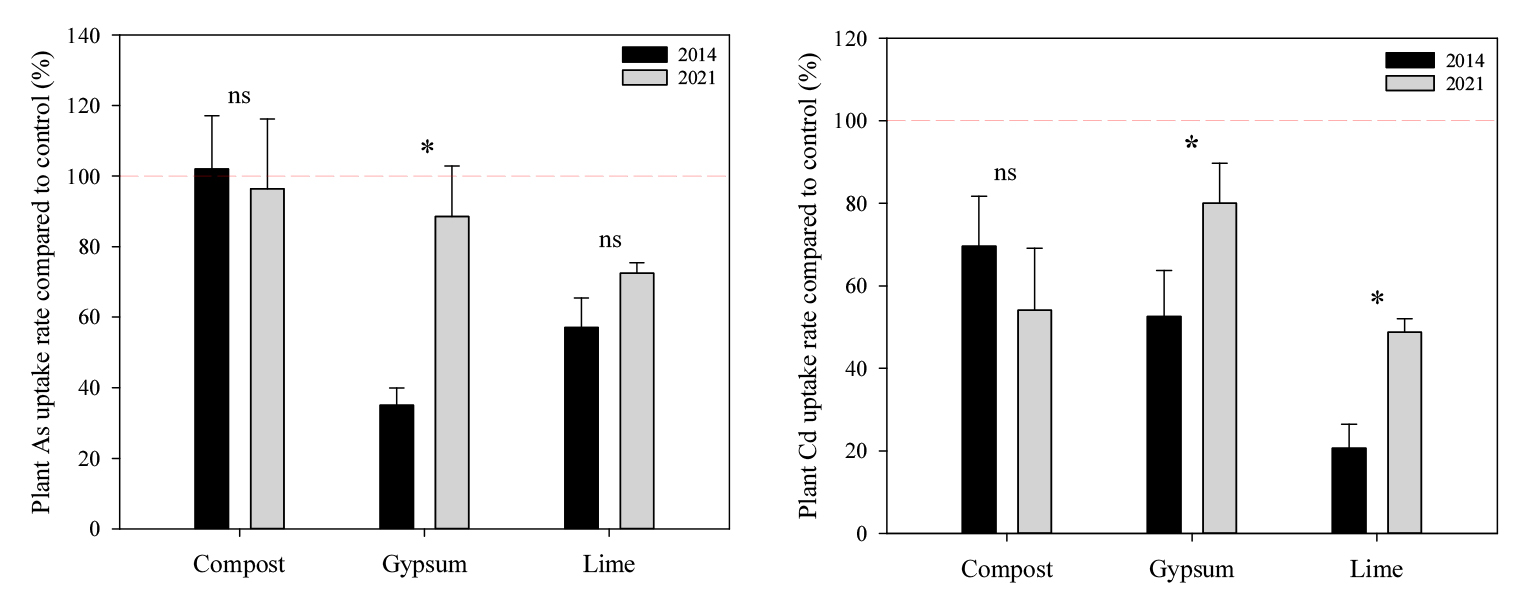
- Efficiency and persistence of compost, gypsum, and lime for arsenic and cadmium stabilization in contaminated soil
- Namhee Yi, Taehee Baek, Mina Lee, Kwon-Rae Kim
- Stabilization, a remediation technique using amendments, reduces the phytoavailability of heavy metal (loid)s in contaminated soils, aiding agricultural soil restoration. Common amendments …
- Stabilization, a remediation technique using amendments, reduces the phytoavailability of heavy metal (loid)s in contaminated soils, aiding agricultural soil restoration. Common amendments include lime (L), compost (CM), and gypsum (G), each with distinct stabilization mechanisms. Over time, these amendments may degrade, requiring periodic evaluation of their long-term effectiveness. This study evaluated the persistence of stabilization in arsenic (As) and cadmium (Cd) contaminated soils 7 years post-application of CM, G, and L. Initially treated in 2014, the soils were cultivated with Angelica gigas and later with Brassica rapa L. in 2021 without reapplying amendments. Soil pH, electrical conductivity, and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) were analyzed, along with heavy metal uptake. Results showed there was no significant change in soil chemistry or metal uptake in CM treated soil. In G treated soil after 7 years, pH and DOC increased accompanying with As and Cd uptake increased. In the soil treated with L, soil pH decreased slightly, together with As and Cd uptake increased. These results implied that CM maintained stabilization, while G and L showed diminished efficiency over time, indicating the need for reapplication and management for sustained effectiveness. Plant As and Cd uptake rate of each treatment compared to control in 2014 and 2021 (Red dashed line indicates 100% uptake rate of the control plants). Data for 2014 is from Kim et al. (2018a). - COLLAPSE
-
Original research article
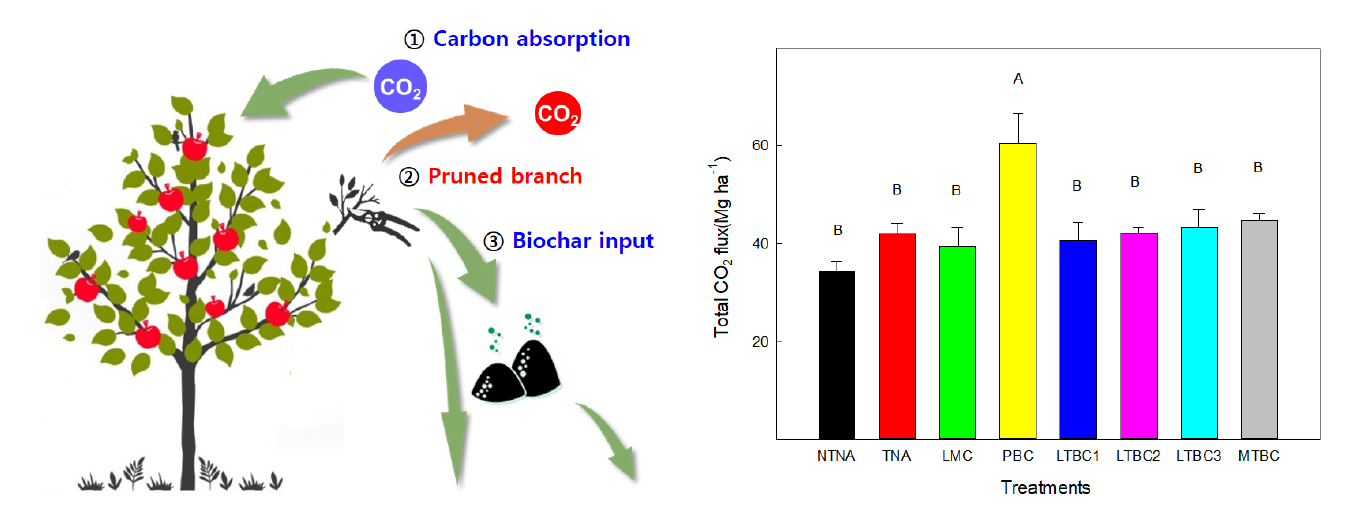
- Effect of biochar and organic amendments on improving soil quality and apple orchard productivity: a 2-year field study
- Periyasamy Rathinapriya, In-Bog Lee, Pyoung-Ho Yi, Seung Tak Jeong
- Soil degradation poses a significant challenge to mature apple orchard productivity. This study aims to investigate the effects of organic amendments on …
- Soil degradation poses a significant challenge to mature apple orchard productivity. This study aims to investigate the effects of organic amendments on soil properties, carbon management, greenhouse gas emissions, apple tree growth and fruit quality in South Korea. We supplied organic amendments, including livestock manure compost (LMC), pruned branch chip (PBC), and three concentrations of low temperature biochar (LTBC; 19.8, 99, 198 m3 ha-1), as well as mid temperature biochar (MTBC) to the mature apple orchard field over two years. Upon various organic amendments, LTBC significantly improved soil physical and chemical properties, enhancing the capacity for cation exchange and water-holding, and reducing bulk density. Moreover, LTBC demonstrated lower CO2 emissions compared to PBC, contributing to effective carbon sequestration and GHG mitigation. No significant differences were observed across treatments on nitrous oxide emissions. Interestingly, both LMC and LTBC boosted apple tree growth, development and fruit yield compared to other organic supplements, which may contribute to enhancing fruit nutrient contents. These findings highlight LTBC’s ability to improve soil carbon storage and nutrient retention due to its high stability and resistance to decomposition. Identifying key organic amendments from this study will pave a way for reducing dependence on chemical fertilizers while enhancing orchard productivity. This study lays the groundwork for more research into how organic amendments work together and whether they are cost-effective for large-scale use, which will help apple production last and restore the soil. Organic amendment LTBC enhanced soil properties, carbon sequestration, and reduced GHG emissions, while LMC and LTBC boosted apple tree growth and yield. - COLLAPSE
-
Original research article
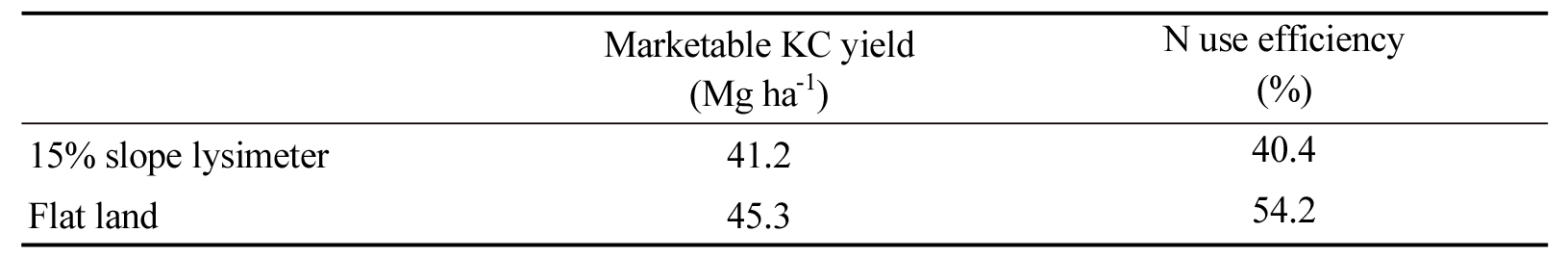
- Optimizing fertilizer use efficiency for Kimchi cabbage production in Highland Agriculture: Comparing slow and fast release fertilizers on varying slopes
- Mavis Badu Brempong, Yang-Min Kim, Gye-Ryeong Bak, Jeomsoon Kim, Sumi Kim, Jeong-Tae Lee
- Steep slopes in Gangwon’s highland agriculture landscape accelerate soil erosion; reducing fertilizer efficiency and limiting Kimchi cabbage (KC) productivity. This study evaluated …
- Steep slopes in Gangwon’s highland agriculture landscape accelerate soil erosion; reducing fertilizer efficiency and limiting Kimchi cabbage (KC) productivity. This study evaluated the performance of KC, KC nitrogen (N) content, uptake and use efficiency, and post-harvest soil fertility under slow-release (SRF) and fast-release (FF) fertilizer treatments across two slope gradients (15% slope lysimeter and flatland) in 2024. Both SRF and FF significantly improved plant growth and marketable yields compared to the ‘no-fertilizer’ control (NF), with no significant differences between the two fertilizers. Despite SRF supplying higher phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) doses, similar N levels in both treatments led to comparable N content, uptake and yield outcomes. Plant weight and head height were greater in the flatland, likely due to improved water retention and higher baseline soil fertility. Soil losses recorded in slope lysimeters under SRF and FF were lower than previous records, and did not significantly affect N availability or uptake. However, NUE was reduced in the slope lysimeter, likely due to other less favorable soil conditions. SRF proved promising in sloped environments, potentially due to its slow nutrient release mechanism, enhancing nutrient retention. The findings indicate the importance of terrain-specific fertilizer management, with SRF offering additional benefits in erosion-prone areas. Future studies should investigate long-term impacts of repeated fertilizer use under varying topographies, focusing on nutrient cycling, soil health, and environmental sustainability. Mean marketable Kimchi cabbage (KC) yield and nitrogen (N) use efficiencies in a 15% slope lysimeter and flatland. Marketable KC yield (Mg ha-1) N use efficiency (%) 15% slope lysimeter 41.2 40.4 Flat land 45.3 54.2 - COLLAPSE
-
Original research article
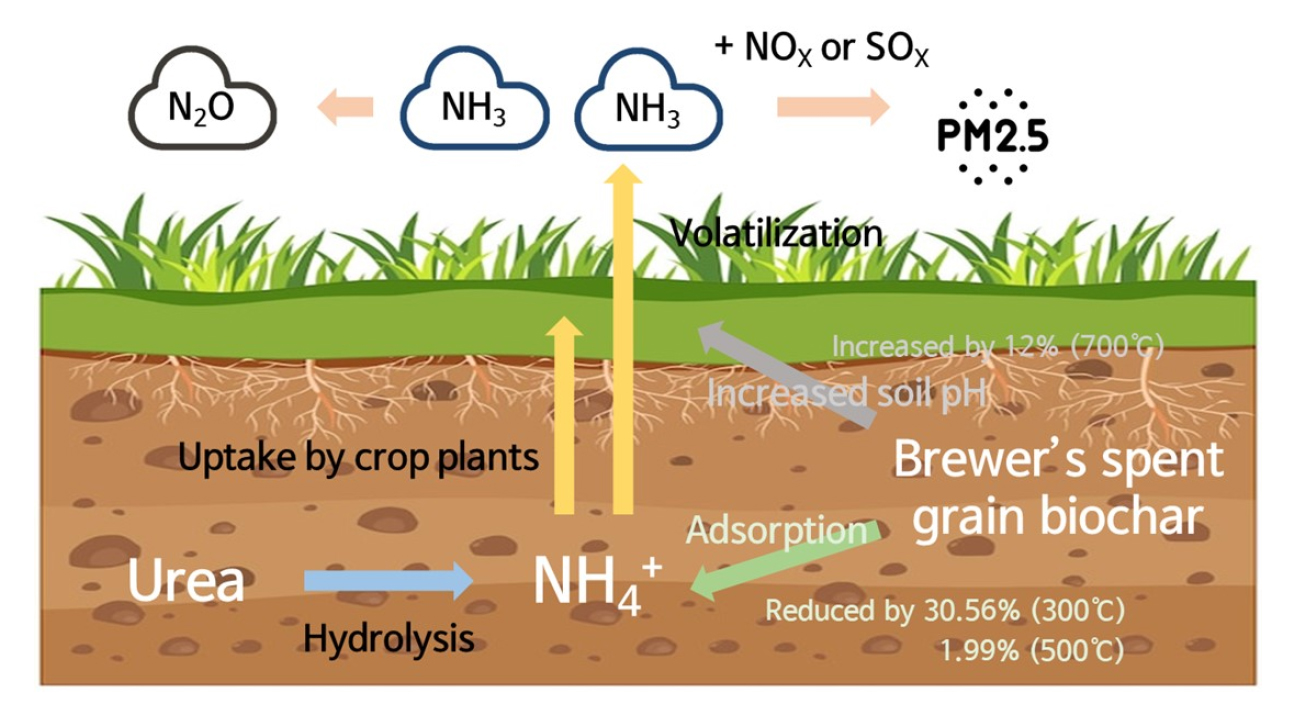
- Potential role of pyrolysis temperature for brewer’s spent grain biochar on mitigating ammonia emissions from urea-fertilized soils
- Yun-Gu Kang, Jun-Ho Kim, Jun-Yeong Lee, Ji-Hoon Kim, Jiwon Choi, Taek-Keun Oh
- Nitrogen (N) management in urea-fertilized soils is essential for enhancing crop productivity and preventing secondary environmental pollutions. This study aimed to evaluate …
- Nitrogen (N) management in urea-fertilized soils is essential for enhancing crop productivity and preventing secondary environmental pollutions. This study aimed to evaluate the potential role of pyrolysis temperature for biochar production and its effect on ammonia (NH3) volatilization and soil chemical properties. The biochar was produced by brewer’s spent grain (BSG) and pyrolyzed at 300°C, 500°C, and 700°C, abbreviated as BSG300, BSG500, and BSG700, respectively. The aforementioned biochars were treated at 3% (by soil weight) in urea-fertilized soils. The pH and nutrient content of BSG biochars were improved by the increase in the pyrolysis temperature from 300°C to 700°C, whereas the EC value was the lowest in BSG700 at 0.71 d‧Sm-1. Additionally, total carbon content of BSG biochars had the positive correlation with the pyrolysis temperature, resulting from BSG300, BSG500, and BSG700 were represented the 59.40%, 66.12%, and 69.23%, respectively. The soil chemical properties represented the similar trend with the chemical characteristics of BSG biochars, and the soil pH and organic matter content in the BSG700 treatment were the highest at pH 6.54 and 4.02%, respectively. However, despite the BSG biochar treatment, the soil pH, exchangeable Ca2+, and exchangeable Mg2+ contents in the BSG300 and BSG500 treatments did not exhibit the statistically significant differences with the initial soil. The NH3 volatilization decreased significantly by the BSG300 and BSG500 amendments at 7.34 kg‧ha-1 and 10.36 kg‧ha-1, respectively, while the BSG700 treatment (11.83 kg‧ha-1) was 1.12-fold higher than urea-only treatment (10.57 kg‧ha-1). Therefore, although BSG300 had the relatively low improvement in soil fertility and carbon sequestration, the BSG biochars pyrolyzed at below 500°C were recommended for effectively N management in urea-fertilized soils. Ammonia (NH3) volatilization by urea-fertilization and mechanisms of brewer’s spent grain biochar for NH3 mitigation in agricultural soils. - COLLAPSE
-
Original research article
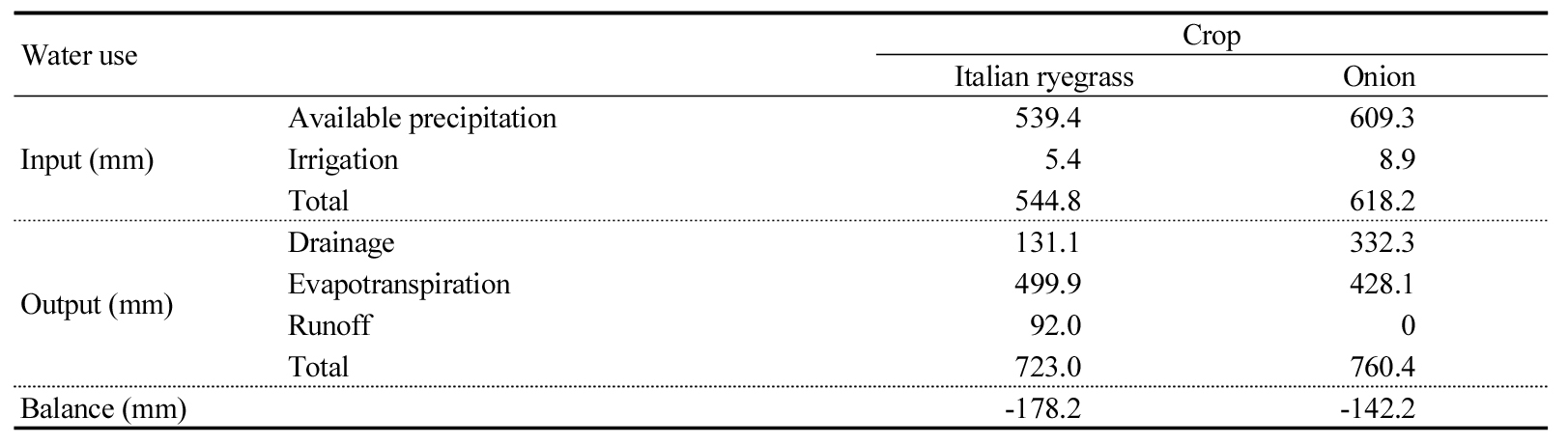
- Assessment of evapotranspiration and water balance during winter onion and Italian Ryegrass cultivations in monolithic weighable lysimeters with sandy loam texture
- Hyun-Seo Yang, Dong-hyun Kim, Seung-oh Hur, Min-kyeong Park, Jung-hun Ok, Woo-Jung Choi
- Assessment of water requirement through water balance analysis is important for efficient irrigation for crop cultivation. However, most relevant studies have been …
- Assessment of water requirement through water balance analysis is important for efficient irrigation for crop cultivation. However, most relevant studies have been conducted for the summer crops, thus relevant information on the winter crops is rare. In this study, water balance was analyzed and water requirement was estimated for the winter crops of paddy (Italian ryegrass, Lolium multiflorum Lam.) and upland (onion, Allium cepa L.) using lysimeter systems from October 2023 to June 2024. During the study period, the available precipitation was 539.4 mm for paddy and 609.3 mm for upland, respectively. Drainage through percolation was higher for upland than paddy soils by 200 mm. This is because upland soils had more macro-pore and thus soil water retention capacity is lower and drainage rate is faster compared to paddy soils. The evapotranspiration was higher for paddy than for uplands by 60 mm due to 5-foild higher crop biomass of Italian ryegrass than that of onion. Runoff was 92 mm for paddy, whereas no runoff was in upland, resulting in more negative water balance for paddy (-178.2 mm) compared to that for upland (-142.2 mm). The water requirement was estimated to be 308.5 mm and 287.2 mm for Italian ryegrass and onion, respectively. In this study, the water requirement was lower than the available precipitation during the experimental period, thus precipitation was not limited. However, the water requirement might be affected by the initial soil water content and weather conditions; therefore, it is necessary to design irrigation scheme by considering both soil water characteristics and the weather conditions. Water balance of Italian ryegrass and onion in winter season from 2023 to 2024 using lysimeters. Water use Crop Italian ryegrass Onion Input (mm) Available precipitation 539.4 609.3 Irrigation 5.4 8.9 Total 544.8 618.2 Output (mm) Drainage 131.1 332.3 Evapotranspiration 499.9 428.1 Runoff 92.0 0 Total 723.0 760.4 Balance (mm) -178.2 -142.2 - COLLAPSE
-
Original research article
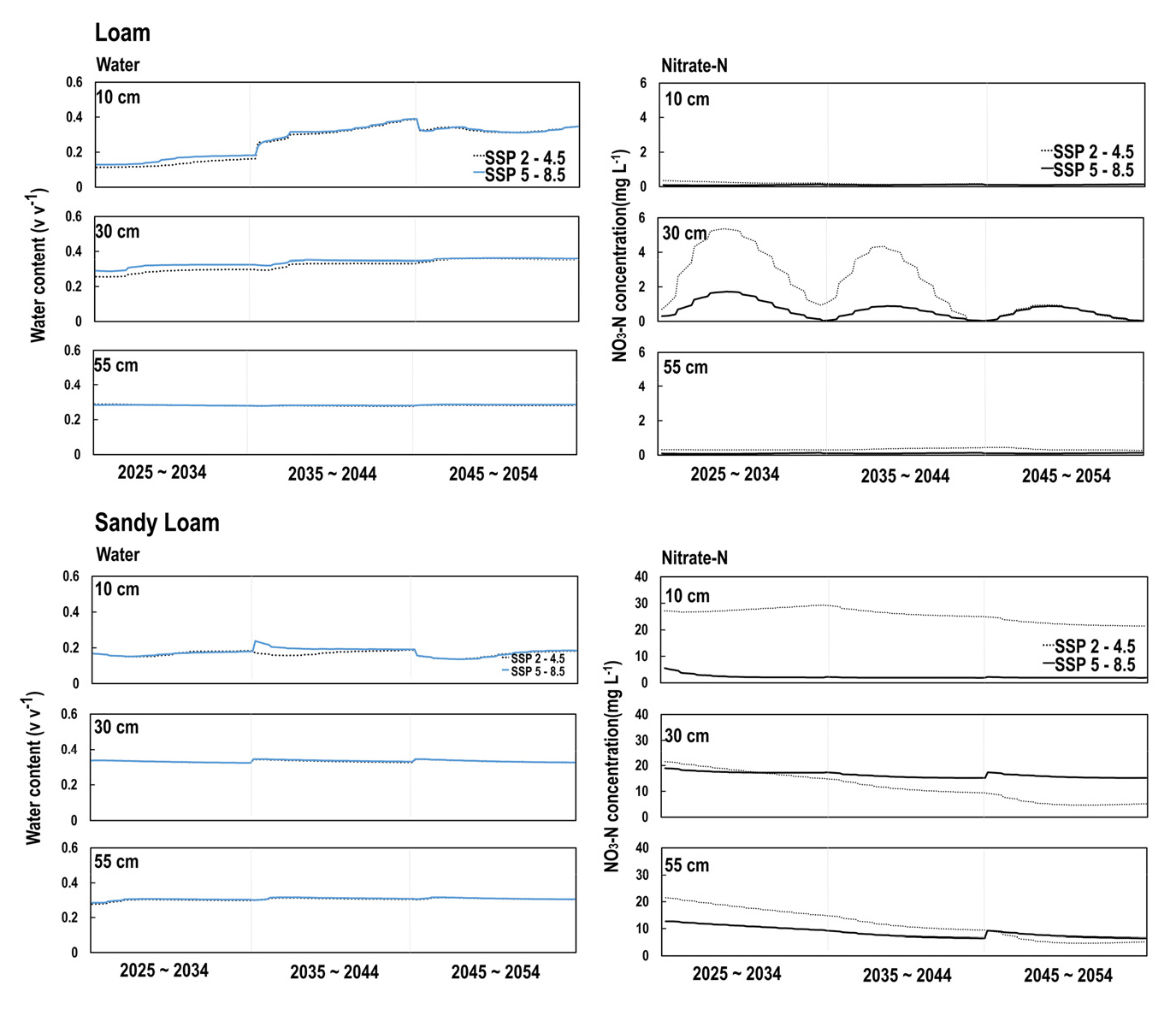
- Assessing nitrogen transport through soil layers in weighable lysimeter under climate change scenarios using HYDRUS1D model
- Minji Kim, Taeil Jang, Donghyun Kim, Junghun Ok, Chanwook Lee, Yejin Lee
- Field monitoring is often limited by factors such as time, labor, weather, crop types, and soil properties. To overcome these limitations, process-based …
- Field monitoring is often limited by factors such as time, labor, weather, crop types, and soil properties. To overcome these limitations, process-based modeling can complement field observations. This study evaluated soil moisture dynamics and nitrate-N leaching using data from weighable lysimeters and the one-dimensional HYDRUS-1D model, incorporating future climate scenarios (SSP2-4.5 and SSP5-8.5) to assess potential impacts under projected climate conditions. Model performance was evaluated using the Coefficient of determination (R2), Willmott’s index of agreement (d), and the Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE). HYDRUS-1D showed good agreement between observed and simulated soil water content and nitrate-N concentration. Soil moisture content in loam soils, R² ranged from 0.37 to 0.72, d from 0.18 to 0.40, and NSE from 0.13 to 0.59. In sandy loam, values were higher: R² from 0.52 to 0.77, d from 0.27 to 0.47, and NSE from 0.39 to 0.67. Nitrate-N concentrations were accurately predicted at all depths in loam and at 30 cm in sandy loam. Short-term simulations (2025 - 2054) under Shared Socioeconomic Pathway (SSP) 2-4.5 and Shared Socioeconomic Pathway (SSP) 5-8.5 scenarios showed that soil moisture at 10 and 30 cm depths increased significantly under SSP5-8.5 due to greater rainfall and evapotranspiration. Nitrate-N concentrations gradually declined compared to 2025. In loam, nitrogen leaching remained relatively low overall, with only a slight increase under SSP5-8.5 compared to SSP2-4.5, particularly during heavy rainfall. In sandy loam, however, nitrogen leaching was consistently higher under SSP5-8.5 and gradually over time. These findings underscore the importance of nitrogen management strategies that respond to climate variability. Integrating field monitoring with modeling offers an effective approach for predicting nitrogen dynamics and supporting sustainable fertilizer use under changing climate conditions. Modeling soil moisture content and NO3-N leaching at 10, 30 and 55 cm of soil depths under climate change scenarios using HYDRUS-1D model. - COLLAPSE
-
Original research article
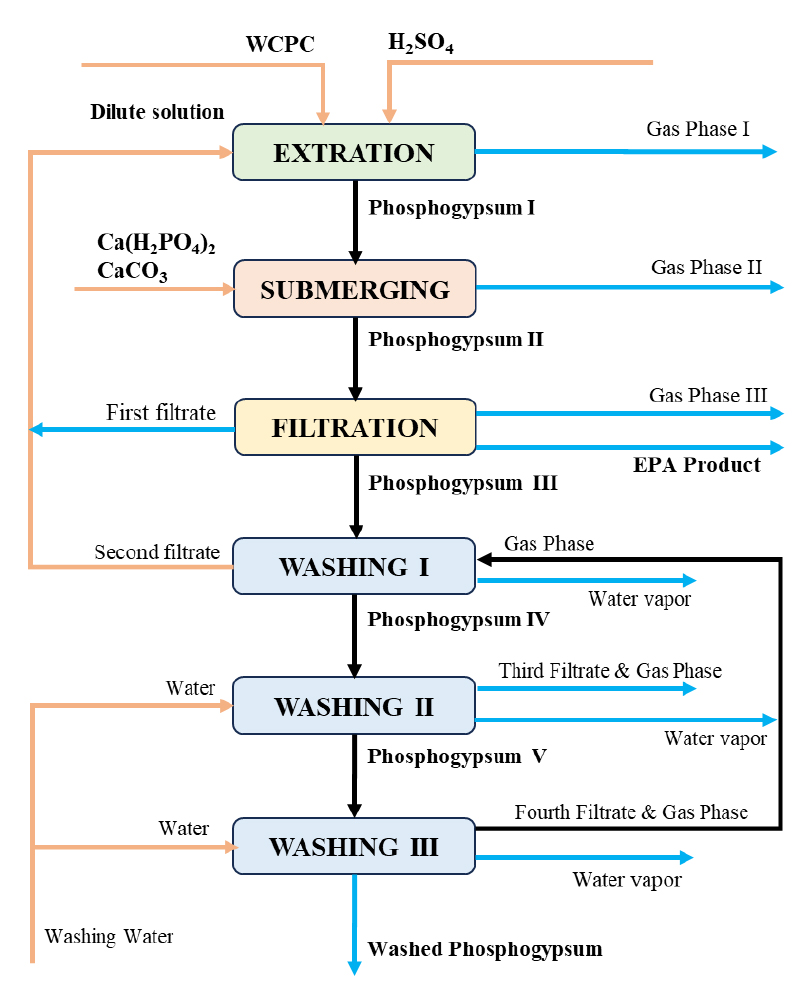
- Simultaneous removal of fluorine and sulfate impurities from phosphoric concentrate using CaCO3 and Ca(H2PO4)2
- Yumrak Oh, Israiljon Turgunovich Shamshidinov, Rixsitilla Yunusali Najmiddinov
- The objective of this study is to investigate the process of producing environmentally safe and highly water- soluble ammonium phosphate by removing …
- The objective of this study is to investigate the process of producing environmentally safe and highly water- soluble ammonium phosphate by removing fluorine and sulfate impurities during the extraction of phosphoric acid from phosphorite in the Central Kyzyl Kum region of Uzbekistan and by purifying associated impurities such as iron, aluminum, calcium, magnesium, sulfate, and fluorine during the ammonization stage of the extracted phosphoric acid. For the analysis of experimental results, chemical and physicochemical methods (spectrophotometry, pH measurement, electron microscopy analysis) were utilized, along with statistical processing of experimental data. By removing fluorine and sulfate impurities during the phosphoric acid extraction process, the technological process was simplified, and by further purifying associated impurities such as iron, aluminum, calcium, magnesium, and fluorine from the extracted acid, the content of P2O5, the key component of the final product, was increased. The research results confirmed that adding calcium carbonate or monocalcium phosphoric to the extracted phosphoric acid (EPA) slurry based on Central Kyzyl Kum phosphorite enables the simultaneous removal of fluorine and sulfate. Furthermore, by completely purifying the partially refined phosphoric acid obtained during the extraction process in the ammonization stage, high-quality, highly water-soluble ammonium phosphate was produced. The resulting product is a fully water-soluble nitrogen-phosphorus fertilizer that can be used as a suitable fertilizer for drip irrigation and hydroponic cultivation of agricultural crops. Flowchart for the production of extracted phosphoric acid (EPA) purified from fluorine and sulphate using carbonate feedstock. - COLLAPSE
-
Original research article
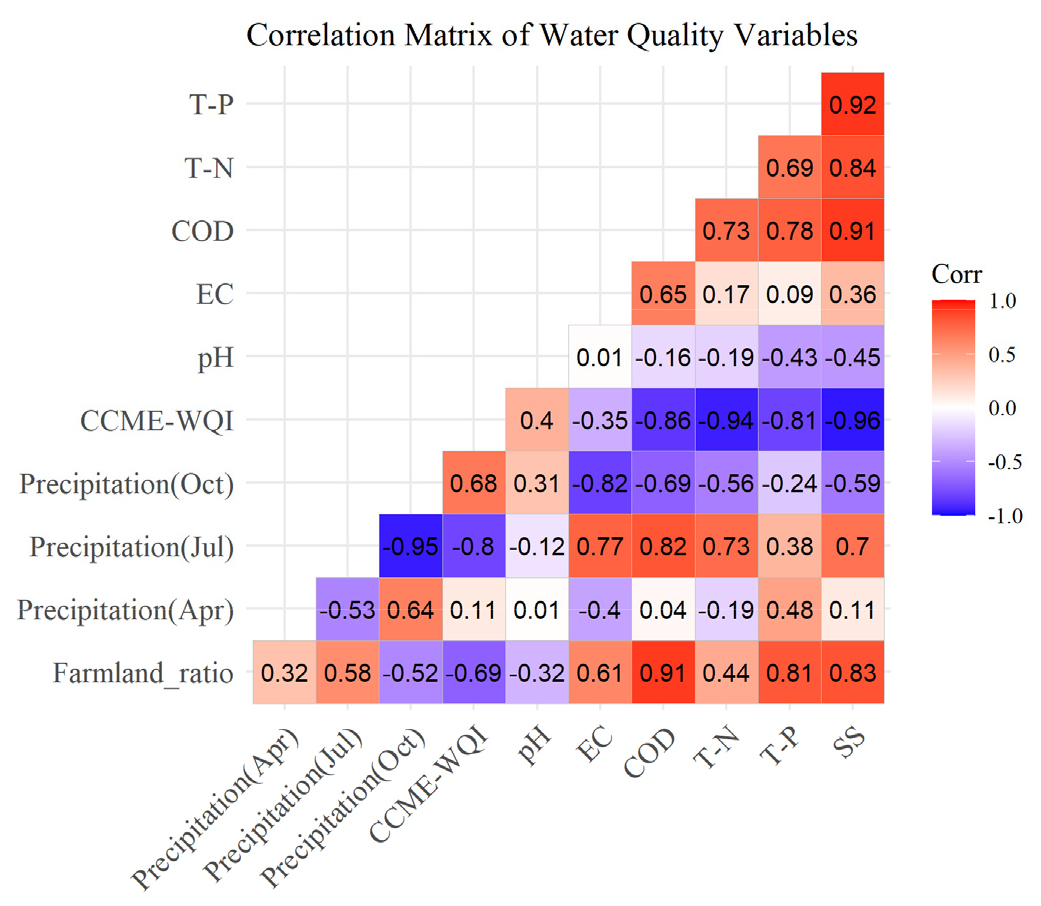
- Evaluation of long-term water quality trends and CCME-WQI applicability in agricultural watersheds of Korea
- So-Jin Yeob, Goo Bok Jung, Byung-Mo Lee, Jaewon Jeong, Min Gyeong Kim, Juhee Yu, Yungi Cho, Na-Young Park, So-Youn Lee, Jong-Hee Shin, Youngmin Jin, Yoon Jeong Ko, Soon-kun Choi
- This study analyzed 10-year (2015 - 2024) trends in water quality parameters and the Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment Water …
- This study analyzed 10-year (2015 - 2024) trends in water quality parameters and the Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment Water Quality Index (CCME-WQI) across five provinces in Korea. The CCME-WQI analysis indicated that Gangwon-do maintained Fair to Good ratings with high stability, while Gyeonggi-do generally fell within the Marginal range. Chungcheong-do showed persistently low water quality, mostly within the Poor range. Jeolla-do exhibited mostly Poor-level quality, and Gyeongsang-do showed moderate variability with Fair-level quality overall. The nationwide average CCME-WQI was approximately 55.7, indicating a marginal water quality level overall. The coefficient of variation (CV) for CCME-WQI was consistently lower than that of individual parameters, supporting its robustness and representativeness as an integrated indicator. Correlation analysis revealed strong positive relationships between farmland ratio and nutrient-related indicators (e.g., CODMn, T-P, SS), and significant negative correlations between CCME-WQI and these pollutants (e.g., SS: r = -0.96). Additionally, cumulative precipitation—particularly in July—showed stronger negative correlations with CCME-WQI (e.g., July: r = -0.80) than the farmland ratio (r = -0.69), suggesting that hydrological variability may exert a more immediate influence on water quality in agricultural watersheds than static land use patterns. These findings suggest that CCME-WQI is an effective tool for long-term water quality evaluation in agricultural watersheds influenced by non-point source pollution. Pearson correlation matrix among CCME-WQI, key water quality parameters, farmland ratio, and cumulative precipitation across five provinces in Korea. - COLLAPSE
-
Short communication
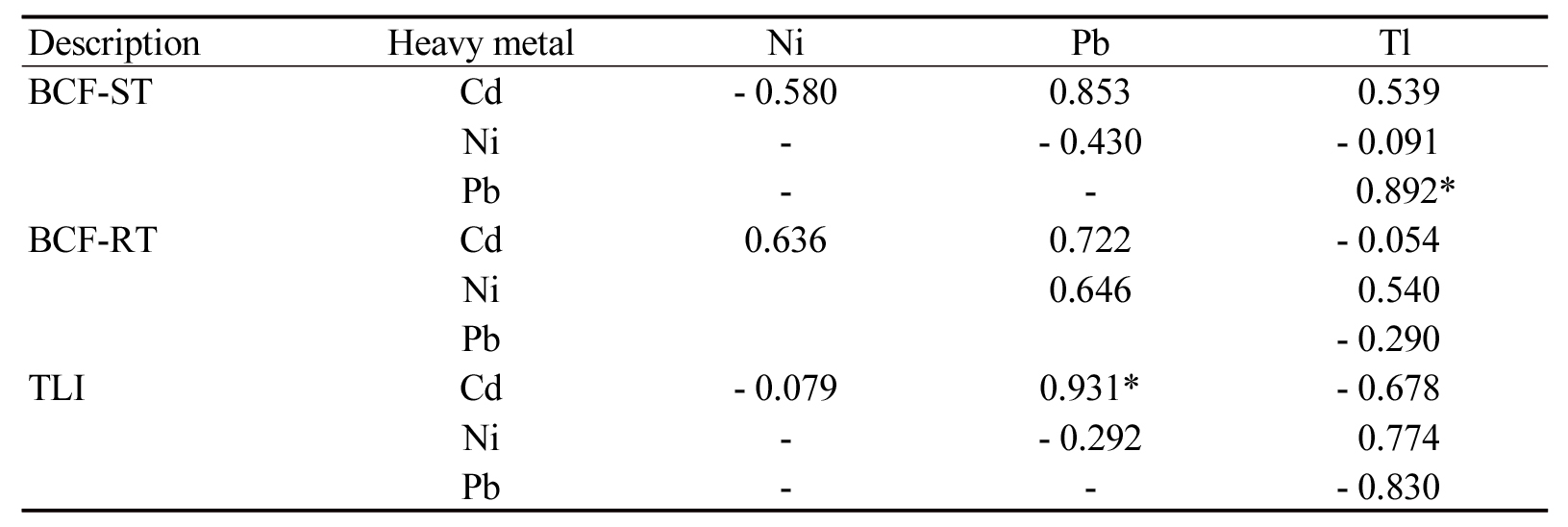
- Comparison of cadmium, nickel, lead and thallium translocation in Malva verticillata L. grown in hydroponic system
- Min Jeong Kim, Young-Mi Seol, Jin-Ho Lee
- A wide range of agricultural lands has been contaminated with various heavy metals, severely impacting food security and human health. In this …
- A wide range of agricultural lands has been contaminated with various heavy metals, severely impacting food security and human health. In this study, we investigated the uptake and translocations of cadmium (Cd), nickel (Ni), lead (Pb), and thallium (Tl), in Malva verticillata L, using different parameters, including bio-concentration factors in shoot and root (BCF-ST and BCF-RT) and the translocation index (TLI), under hydroponic conditions with 0, 5, 15, 30, and 50 mg L-1 of each target metal applied. Metal concentrations ranged from 21.1 mg kg-1 for Pb to 971.1 mg kg-1 for Ni in the shoots, and from 155.1 mg kg-1 for Ni to 2489.7 mg kg-1 for Pb in the roots. Metal accumulation followed the order Ni > Tl > Cd > Pb in the shoots and Pb > Tl > Cd > Ni in the roots. BCF-ST values for Cd, Pb, and Tl declined with increasing metal concentrations, whereas those for Ni tended to increase. Conversely, BCF-RT values for Cd, Ni, and Pb increased, while those for Tl decreased. Cd, Ni, and Pb concentrations in the shoots were positively correlated with their respective root concentrations, and BCF-ST values for these metals were also positively correlated with their corresponding TLI values (p < 0.1 to p < 0.05). Significant positive or negative correlations (p < 0.05 to p < 0.01) were observed among the measured parameters for Tl. Furthermore, BCF-ST values between Pb and Tl, as well as TLI values between Cd and Pb, were positively correlated, both with significance at p < 0.1. Thus, the movement and accumulation of heavy metals in Malva verticillata L. appear to be governed by metal-specific interactions within this plant species. Correlation coefficients (r) for BCF-ST, BCF-RT, and TLI values among Cd, Ni, Pb, and Tl in mallow. Description Heavy metal Ni Pb Tl BCF-ST Cd - 0.580 0.853 0.539 Ni - - 0.430 - 0.091 Pb - - 0.892* BCF-RT Cd 0.636 0.722 - 0.054 Ni 0.646 0.540 Pb - 0.290 TLI Cd - 0.079 0.931* - 0.678 Ni - - 0.292 0.774 Pb - - - 0.830 - COLLAPSE
-
Opinion
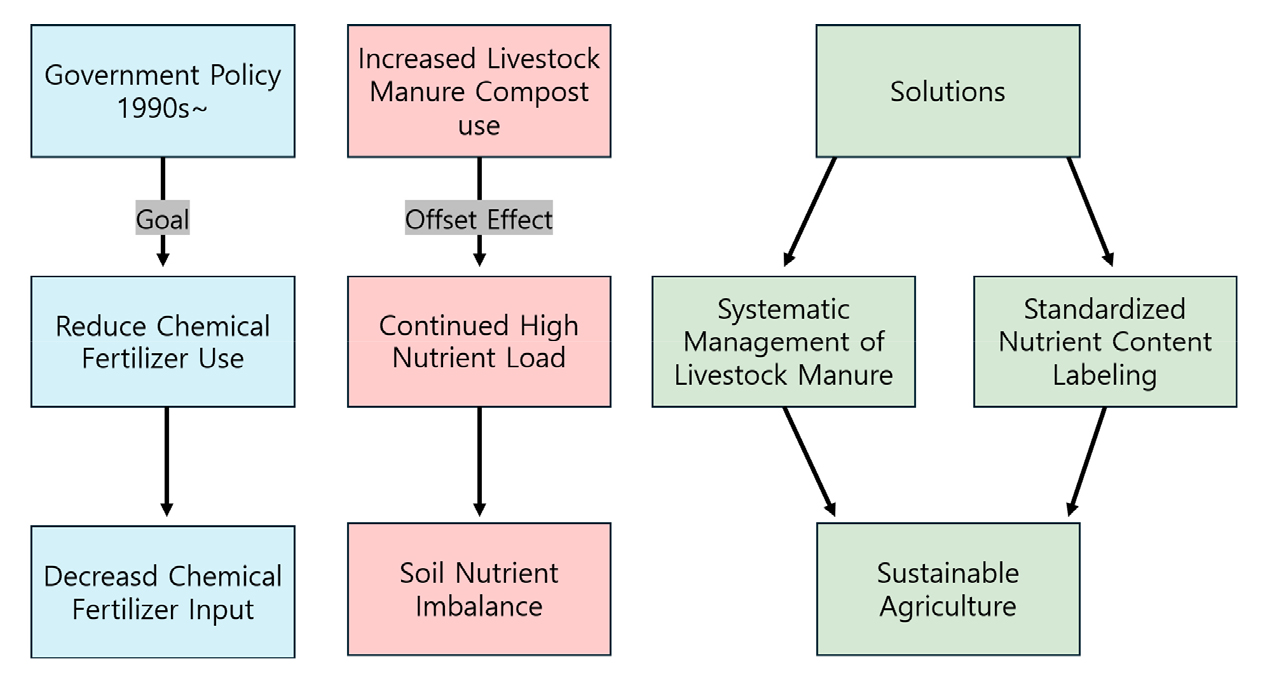
- Changes in soil chemical properties and the impact of livestock manure compost use in Korean agricultural soil: sustainable soil management strategies
- Yong Bok Lee, Kwon-Rae Kim
- This study analyzes the changes in the chemical properties of agricultural land and fertilizer usage in South Korea to propose improvement strategies …
- This study analyzes the changes in the chemical properties of agricultural land and fertilizer usage in South Korea to propose improvement strategies for sustainable agricultural development. Over the past decades, the use of mineral fertilizers has significantly decreased due to government policies aimed at sustainable agriculture. However, despite the reduction in mineral fertilizer usage, the nutrient load in agricultural soils has not improved. This is primarily due to the excessive use of livestock manure compost, which has led to increased levels of available phosphate, potassium, and calcium exceeding optimal levels. Such conditions exacerbate the problem of salt accumulation in soils, potentially having long-term adverse effects on crop growth. To address these issues, this study suggests that the use of livestock manure compost should be systematically managed, taking into account its application rates in fertilization prescriptions. It is essential to standardize and clearly label the nutrient content of livestock manure compost to enable farmers to develop more scientific fertilization plans. This approach can help resolve the issues of salt accumulation and nutrient imbalance in agricultural soils, thereby contributing to the preservation of soil quality and sustainable agricultural development. Issues related to fertilizer and compost policies and future directions. - COLLAPSE
Journal Informaiton
 Korean Journal of Soil Science and Fertilizer
Korean Journal of Soil Science and Fertilizer
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Korean Journal of Soil Science and Fertilizer
Korean Journal of Soil Science and Fertilizer













